Reducing the negative effects of urbanization with a sustainable and participatory approach

Future housing and infrastructure in Ayodhya raise concerns about heat stress
The city of Ayodhya is known as a temple city and attracts tens of thousands of pilgrims daily. This makes Ayodhya a rapidly growing city. A new master plan is being created with projects for housing, infrastructure (hotels, hospitals, etc.) and commercial activities. Combined with climate change, unwanted heat stress can increase both within the built-up area and in the surrounding regions. Therefore, it is important for a traditional city like Ayodhya to have a plan to protect the thermal comfort of both residents and visitors.
Advanced tools and education for heat-conscious urban development
Heat-conscious urban development can be achieved using advanced tools for modelling urban growth, monitoring heat stress and analysing scenarios. However, this requires sufficient knowledge and expertise, not only from local government agencies but also from researchers and future urban planners.
In addition to an educational programme to raise awareness about the impact of climate change, tools and technologies for heat-conscious urban development were implemented in collaboration with local students and academics. This approach gives students the opportunity to practice what they have learned in theoretical lessons. As a result, the availability of sufficiently qualified people is increased as quickly as possible.
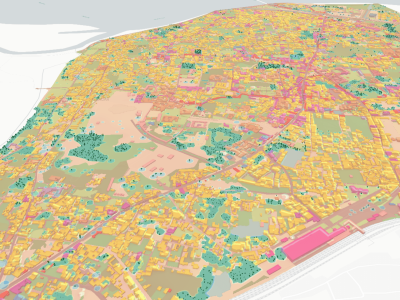
An innovative dashboard has been developed for Ayodhya, containing more than 200 GIS data layers. These data layers are crucial for modelling urban growth simulations up to 2050 and assessing the impact of climate change. These detailed data have served as the basis for extensive heat stress analyses, validated through in-situ thermal comfort measurements. Students of the Faculty of Architecture and Planning (FoAP, AKTU) have been intensively trained and actively involved in data collection for both land use planning and heat stress measurements. The staff has also played a significant role in this process, leading to valuable educational experiences and the development of expertise within the faculty.
Another important aspect of the project was raising awareness about climate change. The FoAP has setup an outreach programme related to climate change (CLICKS), enabling more than 3,000 high school students to participate in hands-on thermal measurements. During the URBCARE conference, organised on 22 - 23 November 2023 in India as part of this project, state officials, students, industry professionals and researchers were informed about adaptation approaches for heat stress. The findings of this international conference have been consolidated in proceedings, contributing to the dissemination of knowledge and best practices.
Another significant outcome of the project is the development of the first Thermal Comfort Action Plan for the city of Ayodhya. This action plan, based on extensive GIS analysis conducted by VITO and FoAP, will serve as a template for other cities aiming to enhance their climate resilience and thermal comfort.